The role of local governments in activities aimed at improving the state of waters in the country
13 lipca 2021 r.
In the times of changing climate, the good condition of the environment, including water, guarantees sustainable development and the safety of using resources, including water. The problem of drinking water shortage and its rationing in the summer period is becoming a problematic, everyday reality. Therefore, the protection of water resources, including groundwater - natural reservoirs of good-quality water, and the improvement of their condition is a goal the achievement of which will ensure water safety. Water retention and delaying its runoff from the catchment area are measures to improve the quantitative status of water. We can only speak of complete success when these waters are in the right quantity and quality, also affecting the condition of aquatic and dependent water ecosystems. Planning activities undertaken in water management meet these expectations. By administering environmental resources at the territorial level, local governments can have a real impact on water protection. Thanks to the implementation of remedial actions resulting from water management plans, they take an active part in the implementation of environmental objectives for the improvement of the state of waters in our country.
Ad hoc and temporary measures can be effective, but the key to a responsible policy for the improvement of waters and ecosystems dependent on waters is the implementation of activities included in the planning documents prepared by the National Water Management Authority. We are talking about the project of the 2nd update of the river basin management plans - IIaPGW, the drafts of which are under public consultation. For more information, visit: www.apgw.gov.pl.
Remedial actions in IIaPGW - a remedy to improve the condition of water in the immediate environment
It will not be possible to achieve proper water status without taking specific actions in the field, therefore assigning specific environmental objectives was preceded by an analysis of the impact of human activity on the condition of water. To solve this problem, sets of corrective action were proposed within IIaPGW - basic and complementary[1], the comprehensive implementation of which will bring about the expected effect for waters. For each measure, units responsible for implementation and implementation schedule were indicated, assigning tasks within IIaPGW to both government and local administration bodies, as well as entities utilizing water services, scientific institutes or institutions operating within the sphere of area nature protection.
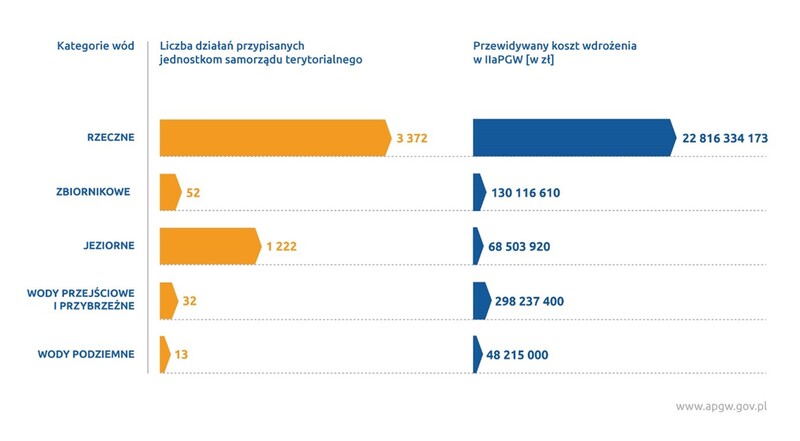
The role of local governments - challenges of water and sewage management to achieve good water status
Activities aimed at local government bodies focus primarily on the municipal economy. Their implementation is crucial for ensuring adequate water quality. Among nationwide activities, municipalities were indicated as units implementing tasks related to the management and designation of agglomerations and the implementation of the national municipal wastewater treatment program, with sets of measures assigned to specific water bodies, with projects including, for example, the construction or modernization of a sewage network or sewage treatment plant in a given city, municipality or agglomeration. This also includes activities related to wastewater management in non-urbanized areas, including technical and economic analyzes of wastewater management, the purpose of which is to reduce the inflow of municipal pollutants to water, or to organize and improve the infrastructure related to wastewater management in the commune outside agglomerations.
The Act on maintaining order and cleanliness in municipalities imposes obligations on local authorities, including records of septic tanks and household sewage treatment plants. The obligation to control the frequency of emptying septic tanks is helpful in planning the development of sewage networks. The frequency and method of getting rid of municipal sewage sludge allows local governments to keep records of household sewage treatment plants, and the implementation of these tasks has an impact on the condition of water at the local level.
Communes are also tasks with informing about the quality of water intended for human consumption, defining a list of swimming areas in the commune and keeping records and updates thereof. In the era of climate change and necessity of water retention, sustainable management of rainwater and gray water, at the level of local government bodies becomes an important activity, the implementation of which will allow for the adaptation of public space at the local level, e.g. to the recurring problems of urban floods. It is worth to note that, thanks to self-purification of water by water and water-dependent ecosystems, investments in blue and green infrastructure also indirectly contribute to the improvement of water quality in the immediate environment.
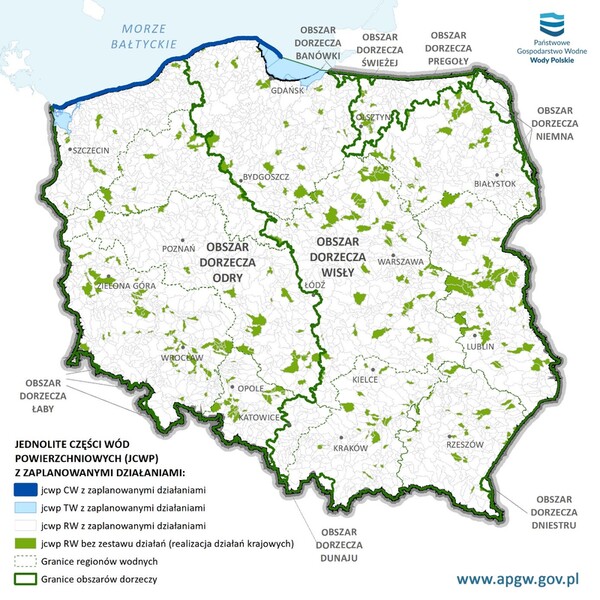
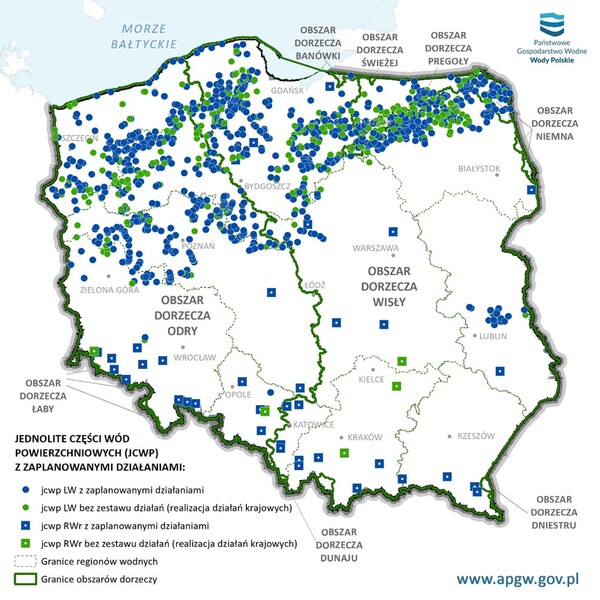
The role of local governments - rehabilitation of water ecosystems in order to achieve their good condition
Good water condition affects not only the tourist attractiveness of a given region, but also makes it a favorable place to live. Although the distribution of lakes in Poland is irregular and closely related to the geological structure and past glaciation, their presence had an impact on the development of infrastructure in a given town or commune and the prospect of further regional economic development. Lake reclamation activities help achieve a good water condition and meet environmental objectives. It is true that such activities are demanding and spread over time, but their implementation brings about tangible results, including environmental and socio-economic benefits. Municipal governments are responsible for monitoring the course and effectiveness of the implemented reclamation activities, promoting responsible and sustainable management of the local water resources.
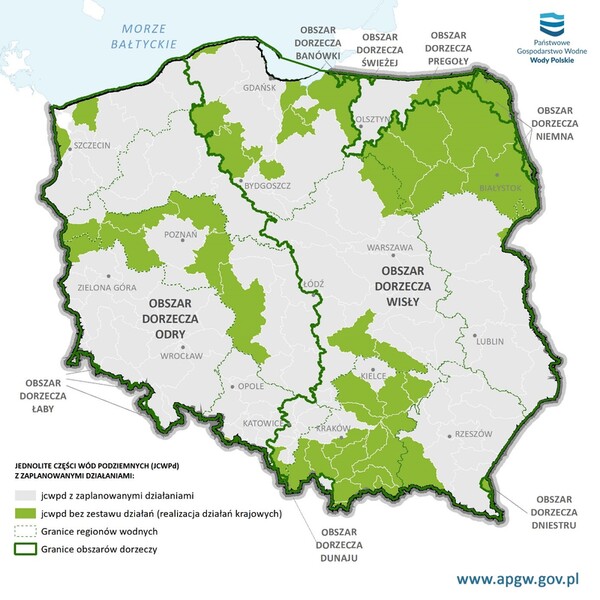
The role of local government bodies in protection and sustainable utilization of groundwater resources
Protection and improvement of water condition, including ground waters, which constitute valuable reservoirs of potable water, is vital in order to secure qualitatively and quantitatively adequate water assets for future generations. Therefore, for a part of municipal governments, in case of activities for certain unified parts of ground waters, activities were prescribed aimed at increasing retention in urban areas, including analyzes and project documentation for the purpose of increasing retention in developed areas, developing and implementation of peatland protection plans, actions aimed at limiting ascent, ingress of salt waters into usable water-bearing levels or building pipelines to transfer waters to facilitate the reconstruction of groundwater levels in sensitive areas - such as post-mining workings.
Benefits from improving the condition of water in the whole country and locally
When thinking about improving the status of waters, we are talking about setting specific goals and a time perspective in which they are to be achieved. It is precisely this action that is one of the key aspects of water management plans with environmental objectives set for water bodies. Data from the state water monitoring still indicates that the condition of Polish waters leaves much to be desired, as the vast majority of waters in our country is in poor condition. This, in turn, influences the possibility of economic or recreational use of waters, translating also into the tourist and residential attractiveness of a given region of the country - each of us wants to live and rest in safe and environmentally valuable places.
The implementation of the Water Framework Directive 2000/60 / EC has been in progress in Poland since joining the European Union. Despite the passage of time, the topic of water quality and quantity is still relevant and particularly important, especially in the context of a changing climate. Therefore, water management plans developed for each river basin district and periodically updated every 6 years are particularly important in the field of rational water management. Preparation of water management plans is preceded by the preparation of planning documentation, including development of lists of water bodies (unit of water)[2] with characteristics, identification of significant anthropogenic pressures and determination of their impact on the condition of surface and groundwater. This is an extremely complex process; its goal is to guide the management of the country's water resources in a way that will lead us to achieve good water status and meet the set environmental goals.
Have your say on water issues!
The public consultations on the 2nd update of water management plans, which end on October 14, 2021, are an opportunity for each of us to influence the shape of water management in our country and our local environment. The adoption of the plans by means of a regulation of the minister responsible for water management will also enforce sets of measures aimed at improving the condition of national water resources, the implementation of which will be the responsibility of various entities, including local governments. Effective cooperation in the matter of water is the only way for our waters to improve, enabling the sustainable use of their resources, putting equal emphasis on economic development and protection of valuable water and water-dependent ecosystems. Only the implementation of all corrective actions will guarantee the improvement of their condition. The list of corrective actions and environmental goals set in IIaPGW for the years 2021-2027 can be found here: www.apgw.gov.pl.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[1]Basic actions are established for all water bodies. They mainly result from other directives listed in Annex VI to the Water Framework Directive, e.g. the directive on: treatment of urban wastewater, nitrates, wild birds or natural habitats. They contain 169 items in the catalog of national activities. Complementary measures are established for water bodies at risk of failing to achieve environmental objectives.
[2]The basic units in water management planning are surface water bodies - jcwp and groundwater - jcwpd. Jcwp are significant water elements such as e.g. a lakes, water reservoirs, rivers or parts thereof, marine coastal transitional waters. Jcwpd is a defined volume of groundwater present within a water-bearing layer or water-bearing layer complex.
Rest news
- There it is! The first plug from The National Water Management Authority is ready for download.
- World Water Day 2022 under the slogan "Making the invisible visible"
- The validity period of the 2016 water management plans was extended until 22.12.2022.
- From plans to action - what awaits the water management in Poland?
- We will not improve the status of water without specific actions
- Public consultations IIaPGW and aPZRP: over 2,000 applications in order to ensure security against flooding and good water condition!